Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a major cause of perioperative morbidity and mortality. Each year 25 000 people in England die from VTE. Without prophylaxis, 40-80 % of high risk patients develop detectable DVTs and up to 10 % die of PE.
Risk factors for VTE include:
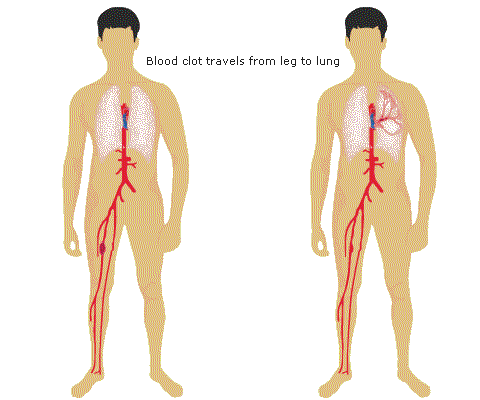
Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a major cause of perioperative morbidity and mortality. Each year 25 000 people in England die from VTE. Without prophylaxis, 40-80 % of high risk patients develop detectable DVTs and up to 10 % die of PE.
Risk factors for VTE include:
Patient factors
- Age >60 years
- Previous DVT, PE, thrombophilia e.g. protein C, S deficiency, Factor V Leiden
- Pregnancy
- Puerperium
- Oestrogen therapy (HRT, oral contraceptive pill (OCP))
- Obesity (BMI >30 kg/m2)
- Immobility
- Continuous travel of >3 h approximately 4 weeks before/after surgery

Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a major cause of perioperative morbidity and mortality. Each year 25 000 people in England die from VTE. Without prophylaxis, 40-80 % of high risk patients develop detectable DVTs and up to 10 % die of PE.
Risk factors for VTE include:
Associated diseases
- Active heart or respiratory failure
- Acute medical illness/infection
- Recent cerebrovascular event (CVE)/myocardial infarction (MI)
- Varicose veins with phlebitis
- Trauma (especially lower limb fractures or spinal injury)
- Haematological diseases, e.g. paraproteinaemia
- Nephrotic syndrome
- Inflammatory bowel disease (Crohn’s or UC)

Venous thromboembolism (VTE) is a major cause of perioperative morbidity and mortality. Each year 25 000 people in England die from VTE. Without prophylaxis, 40-80 % of high risk patients develop detectable DVTs and up to 10 % die of PE.
Risk factors for VTE include:
Operation factors
- Surgery lasting <30 min is considered minor (low risk)
- Surgery lasting >30 min is considered major (higher risk)
- Types of surgery considered high risk include major joint replacements, hip fracture surgery and surgery to the abdomen and pelvis
NB: Any patient confined to bed is at risk of VTE.
