Introduction
The normal electrolyte requirements are:
Na+ 1-2 mmol/kg/24 h and K+ 0.5-1 mmol/kg/24 h.
The Na+ and K+ concentrations are very important in determining the fluid shifts and also the deficits or excesses in a patient.
The kidneys control the electrolyte composition (ignoring losses through the sweat and the GI tract) and, as water largely follows sodium ions, they also control the fluid composition of the body.
Important information about the movement between the compartments is considered on the next tab.
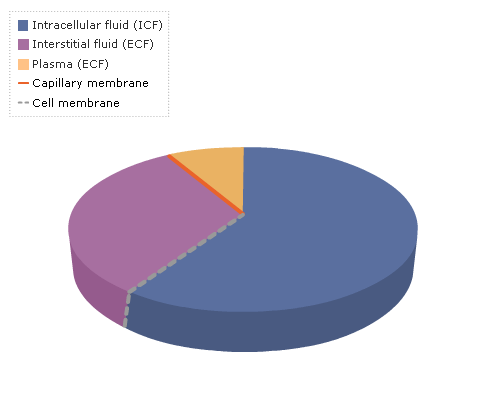
Chart 1 Cell and capillary membranes