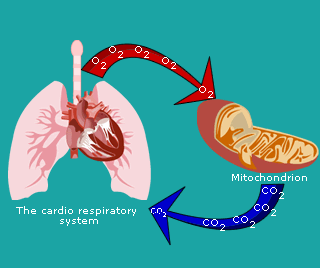
The body’s cells require an adequate supply of oxygen (O2) in the blood. This delivery (the oxygen flux) is dependent on the:
- Oxygen content of the blood
- Cardiac output
Oxygen content
When fully saturated 1 g of Hb holds 1.34 mL oxygen. Assuming a Hb concentration of 150 g/L (15 g/dL), we can calculate the oxygen content in arterial blood (CaO2).
CaO2 = Hb-bound + dissolved
= ([Hb] × 1.34 × satn) + (0.23 × PO2)
= (150 × 1.34 × 0.98) + (0.23 × 13)
= 197 + 3
= 200 mL/L
Oxygen flux
Multiplying the CaO2 by the cardiac output (5 L/min) gives the oxygen flux.
200 × 5 = 1000 mL/min