Displacement of Carina and Heart
The diaphragm and chest contents are displaced cephalad as pregnancy advances. The AP diameter of the chest increases to accommodate this movement.
The clinical implications of this are that the distance from teeth to carina is shortened and the risk of endobronchial intubation is increased. Care must be taken to avoid this.
The heart is enlarged, resulting in changes to the radiographic appearances as shown in Fig 1. There are some changes in the ECG during pregnancy: leftward shift of the axis and T wave inversion in lead V2 are common. Fig 2.
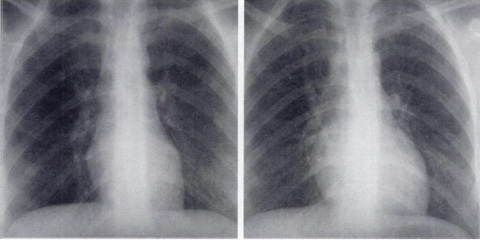
Fig 1 Left-hand slide shows chest radiograph of 24 year old woman with cough, showing normal findings. Right-hand slide one year later – 6 months pregnant - no pneumonia visible but cardiac silhouette larger and pulmonary vessels engorged
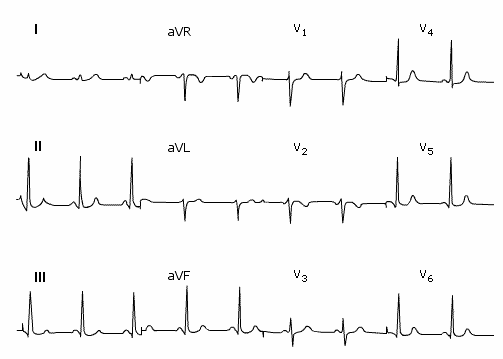
Fig 2 ECG showing T wave changes in late pregnancy in V2