Catheter-through-needle and catheter-over-needle techniques exist for placing catheters into the subarachnoid space. Because of the type of patient in whom this technique is most commonly used and because of the complex technical nature of the procedure, this technique is usually only employed by experienced practitioners.
The same general principles apply as for all of the other neuraxial techniques.
The images show one kit used for the procedure. This is a catheter-through-needle variant.
Catheter-through-needle and catheter-over-needle techniques exist for placing catheters into the subarachnoid space. Because of the type of patient in whom this technique is most commonly used and because of the complex technical nature of the procedure, this technique is usually only employed by experienced practitioners.
The same general principles apply as for all of the other neuraxial techniques.
The images show one kit used for the procedure. This is a catheter-through-needle variant.
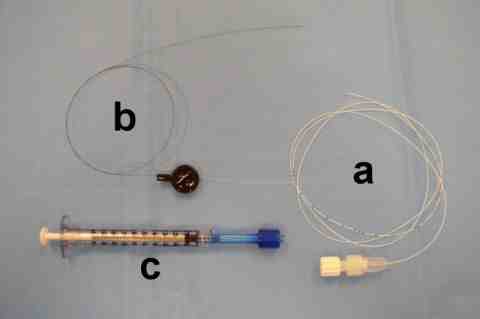
Fig 1 shows three important components of the kit: (a) the microspinal catheter with detachable hub, (b) the obturator, which confers rigidity on the catheter to permit threading through the needle and (c) the 1 mL syringe, which is required for accuracy of dosing and to generate sufficient pressure to inject through the long, narrow catheter.
Catheter-through-needle and catheter-over-needle techniques exist for placing catheters into the subarachnoid space. Because of the type of patient in whom this technique is most commonly used and because of the complex technical nature of the procedure, this technique is usually only employed by experienced practitioners.
The same general principles apply as for all of the other neuraxial techniques.
The images show one kit used for the procedure. This is a catheter-through-needle variant.
Fig 2 The spinal needle is used to access the subarachnoid space in the normal manner. The catheter (with obturator in place) is threaded through, after which the obturator is removed. Next, the needle is removed over the catheter, before the syringe is connected for injection. The catheter is then secured in place.
