Diagnostic Checks - Machine and Equipment
Perform a quick check of the anaesthetic machine:
- Increase fresh gas flow and FiO2
This compensates for small leaks and should increase alveolar PO2 (Fig 1) - Manual ventilation
- Monitor check – FiO2, CO2, SpO2
- Check ventilator mode and settings are appropriate
- Check airway pressure and flow monitoring
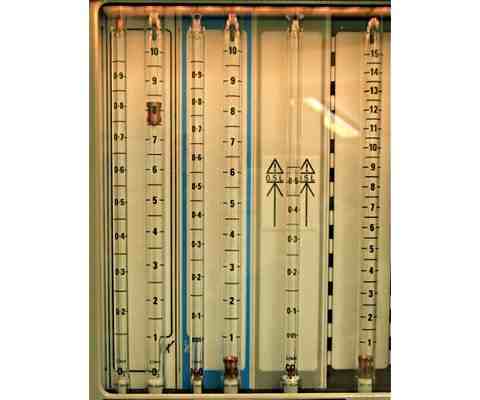

Fig 1 Increase FiO2 and fresh gas flow
Perform a quick check of the anaesthetic machine:
- Increase fresh gas flow and FiO2
- Manual ventilation
Manual ventilation tests both the integrity of the fresh gas delivery system and the patient’s respiratory compliance (Fig 2) - Monitor check – FiO2, CO2, SpO2
- Check ventilator mode and settings are appropriate
- Check airway pressure and flow monitoring
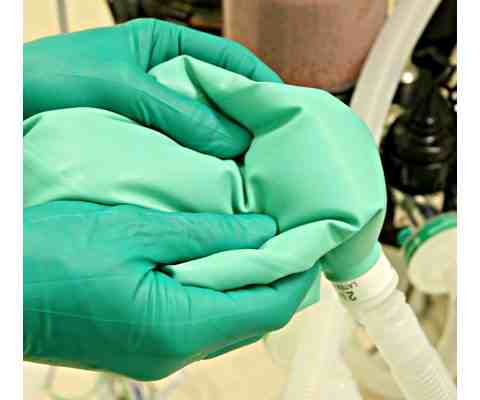

Fig 2 Reservoir bag being manually squeezed
Perform a quick check of the anaesthetic machine:
- Increase fresh gas flow and FiO2
- Manual ventilation
- Monitor check – FiO2, ETCO2, SpO2 (Fig
3)
1. FiO2 - Analyzed in the breathing circuit as close to the patient as possible
2. Capnography - Gives immediate information, for example:- Flat line - Complete failure of ventilation
- Notched trace - Patient respiratory effort during IPPV
- Slow rising initial phase - Upper airway obstruction
- Slow rising “plateau” phase - Bronchospasm
- Check ventilator mode and settings are appropriate
- Check airway pressure and flow monitoring
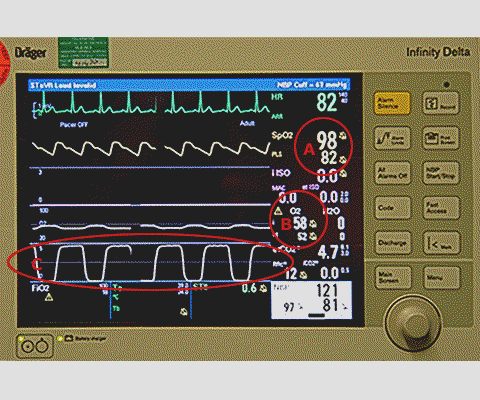
Fig 3 Datex monitor screen, FiO2, CO2, SpO2
Perform a quick check of the anaesthetic machine:
- Increase fresh gas flow and FiO2
- Manual ventilation
- Monitor check – FiO2, CO2, SpO2
- Check ventilator mode and settings are appropriate (Fig 4)
- Check airway pressure and flow monitoring
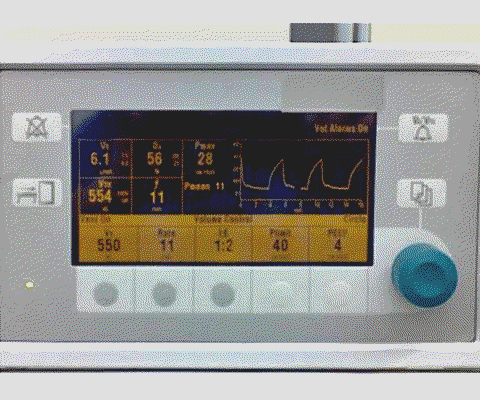
Fig 4 Ventilator setting panel
Perform a quick check of the anaesthetic machine:
- Increase fresh gas flow and FiO2
- Manual ventilation
- Monitor check – FiO2, CO2, SpO2
- Check ventilator mode and settings are appropriate
- Check airway pressure and flow monitoring (Fig
5)
A rising inflation pressure indicates a fall in compliance or an obstructive airway problem
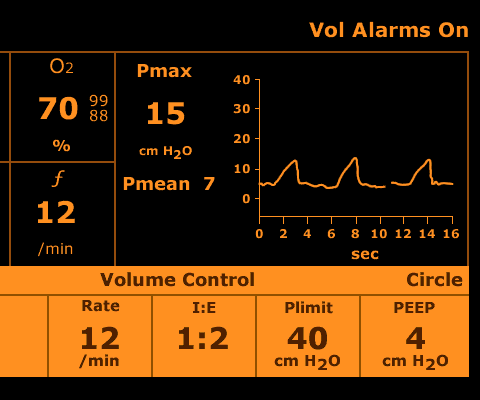
Fig 5 Ventilator pressure waveform