Neurological
Raised intracranial pressure may lead to hypertension. This is part of a cerebroprotective mechanism aiming to maintain cerebral perfusion pressure (CPP) of 60-70 mmHg.
CPP = MAP – ICP (if ICP >
JVP)
CPP = MAP – JVP (if ICP < JVP)
MAP - Mean arterial pressure (mmHg)
ICP - Intracranial pressure (mmHg)
JVP - Jugular venous pressure (mmHg)
From this equation, it can be seen that a patient with raised ICP of 20 mmHg, requires a MAP of at least 90 mmHg to achieve CPP of 70 mmHg. In this case, reducing MAP below 90 mmHg will be detrimental.
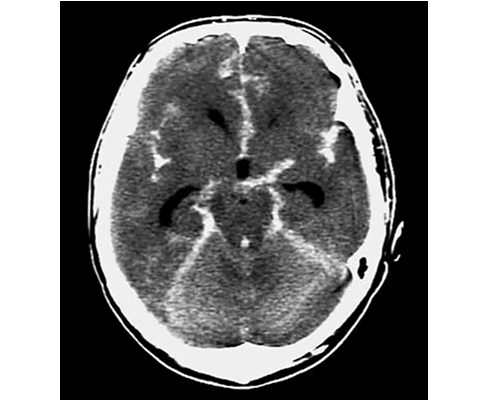
Fig 1 A patient with a subarachnoid haemorrhage, as shown on the CT scan, has raised intracranial pressure and requires a higher MAP to maintain CPP