The Unconscious Patient
A reduced conscious level has many causes and is a risk to the patient's airway and breathing.
Problems include:
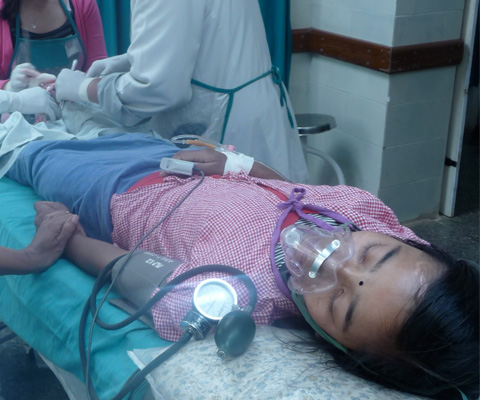

Identifying the unconscious patient
The 'AVPU' system allows rapid assessment of decreased conscious level. The patient falls into one category:
- Alert
- Responsive to Voice
- Responsive to Pain (for example a sternal rub)
- Unresponsive
The Glasgow coma score (GCS) is a score between 3 and 15 based on:
- Eye opening (scores 1 – 4)
- Best motor response (scores 1 – 6)
- Verbal response (scores 1 – 5)
An AVPU of P or U or GCS <8 indicates the patient is unconscious and requires airway protection.
Glasgow coma score (GCS)
The GCS chart is shown in Table 1.
| Eye opening | Motor response | Verbal response | |||
| Spontaneous | 4 | Obeys commands | 6 | Orientated | 5 |
| To voice | 3 | Localizes pain | 5 | Confused | 4 |
| To pain | 2 | Flexion to pain | 4 | Inappropriate words | 3 |
| None | 1 | Abnormal flexion | 3 | Sounds | 2 |
| Extension | 2 | None | 1 | ||
| None | 1 | ||||
Table 1 Glasgow coma score
Risks to the unconscious patient
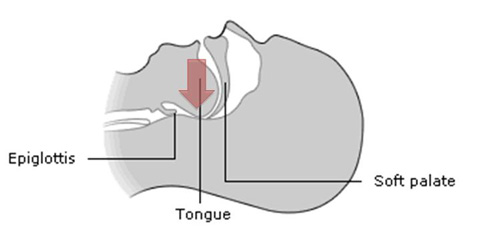
Airway obstruction may occur in the unconscious patient.
Tone of the tongue is lost causing it to drop onto the pharyngeal wall, obstructing the airway.
Protective airway reflexes are also diminished.
The unconscious patient is at risk of aspiration pneumonia.
Causes of loss of consciousness
There are many causes of loss of consciousness. Common causes include:
- Head injury
- Seizures
- Hypoglycaemia
- Infection (such as meningitis or encephalitis)
- Cerebral neoplasm (primary or more commonly secondary)
- Drugs
- Profound hypoxia, hypercapnia or hypotension
Management of the unconscious patient
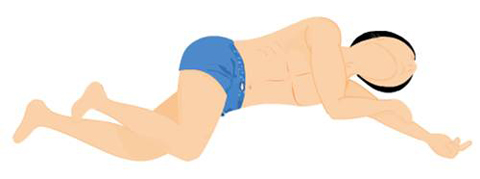
The airway should be opened with head tilt, chin lift and jaw thrust. High-flow oxygen should be given. If advanced life support is not available, the patient should be placed on their side in the recovery position.