Overview
The muscles of the larynx are composed of the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles.
The extrinsic muscles work with other muscles attached to the hyoid to move the larynx up and down during swallowing.
The intrinsic muscles open the vocal cords during inspiration, close the cords and laryngeal inlet during swallowing and alter the tension of the cords during phonation (Fig 1).
The functions of the following muscles should be understood:

The muscles of the larynx are composed of the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles.
The extrinsic muscles work with other muscles attached to the hyoid to move the larynx up and down during swallowing.
The intrinsic muscles open the vocal cords during inspiration, close the cords and laryngeal inlet during swallowing and alter the tension of the cords during phonation (Fig 1).
The functions of the following muscles should be understood:
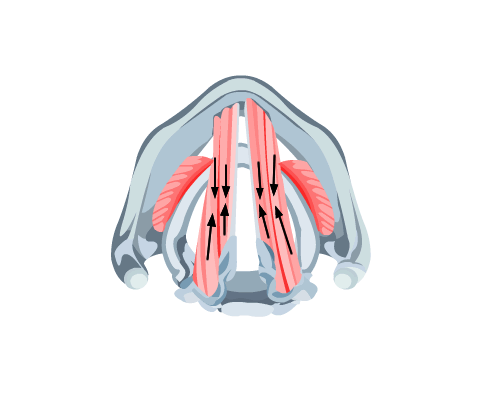
- Posterior cricoarytenoids
These muscles abduct the vocal cords on inspiration. They are the only true abductors. The muscles achieve this by pulling the posterior ends of the arytenoid cartilages together medially. The resulting pivoting movement abducts the anterior ends of the cartilages, to which the vocal cords are attached (Fig 2).
The muscles of the larynx are composed of the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles.
The extrinsic muscles work with other muscles attached to the hyoid to move the larynx up and down during swallowing.
The intrinsic muscles open the vocal cords during inspiration, close the cords and laryngeal inlet during swallowing and alter the tension of the cords during phonation (Fig 1).
The functions of the following muscles should be understood:
- Posterior cricoarytenoids
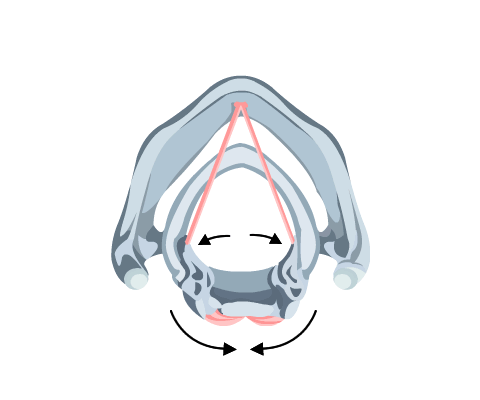
- Lateral cricoarytenoids, transvere arytenoids
These are adductors of the cords and close the vocal cords (Fig 3).
The muscles of the larynx are composed of the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles.
The extrinsic muscles work with other muscles attached to the hyoid to move the larynx up and down during swallowing.
The intrinsic muscles open the vocal cords during inspiration, close the cords and laryngeal inlet during swallowing and alter the tension of the cords during phonation (Fig 1).
The functions of the following muscles should be understood:
- Posterior cricoarytenoids
- Lateral cricoarytenoids, transvere arytenoids
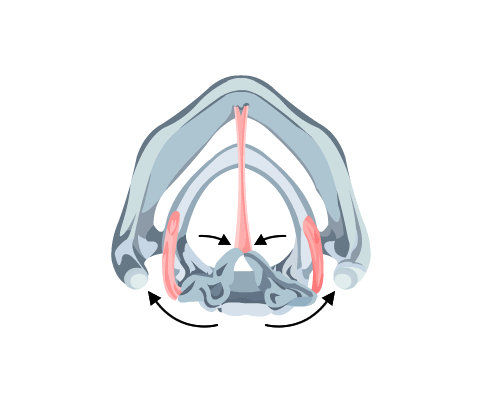
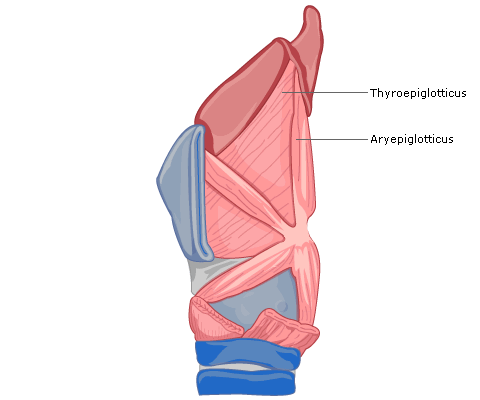
- Aryepiglottics, thyroepiglottics
These are the laryngeal sphincters and close the laryngeal inlet during swallowing (Fig 4).
The muscles of the larynx are composed of the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles.
The extrinsic muscles work with other muscles attached to the hyoid to move the larynx up and down during swallowing.
The intrinsic muscles open the vocal cords during inspiration, close the cords and laryngeal inlet during swallowing and alter the tension of the cords during phonation (Fig 1).
The functions of the following muscles should be understood:
- Posterior cricoarytenoids
- Lateral cricoarytenoids, transvere arytenoids
- Aryepiglottics, thyroepiglottics
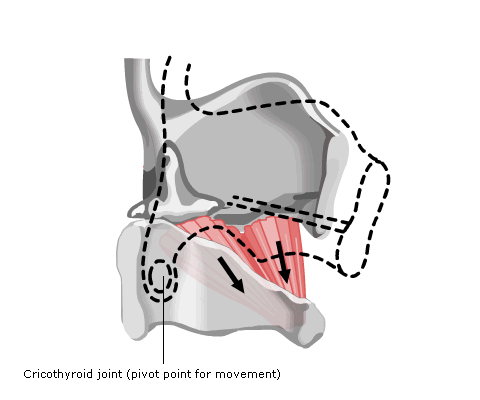
- Cricothyroids
The cricothyroids are the tensors of the cords, acting by tilting the cricoid cartilage (and the attached arytenoids) on the thyroid cartilage (Fig 5).
The muscles of the larynx are composed of the extrinsic and intrinsic muscles.
The extrinsic muscles work with other muscles attached to the hyoid to move the larynx up and down during swallowing.
The intrinsic muscles open the vocal cords during inspiration, close the cords and laryngeal inlet during swallowing and alter the tension of the cords during phonation (Fig 1).
The functions of the following muscles should be understood:
- Posterior cricoarytenoids
- Lateral cricoarytenoids, transvere arytenoids
- Aryepiglottics, thyroepiglottics
- Cricothyroids
- Thyroarytenoids, vocalis
The thyroarytenoids are relaxors of the cords. The vocalis are responsible for the fine adjustment of the cords (Fig 6).