Spontaneous Breathing
Flow along a pathway results from a difference in pressure (ΔP) between one end to the other. This can occur from either an upstream rise or a downstream fall in pressure.
When breathing spontaneously, inspiratory flow occurs by creating a small negative pressure in the alveoli (~ 2-3 cm H2O below atmospheric).
This is brought about by contraction of the diaphragm and external intercostals.
Question: What generates the positive pressure in the alveoli for expiration?
Click here for answer.
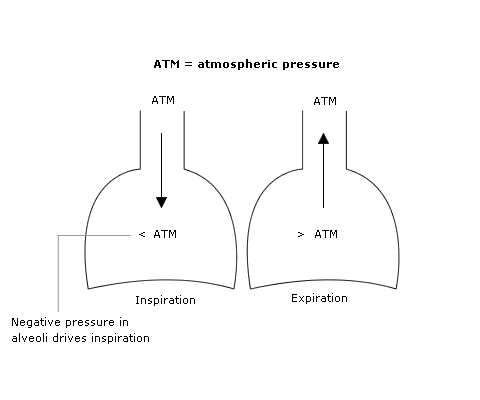
Flow along a pathway results from a difference in pressure (ΔP) between one end to the other. This can occur from either an upstream rise or a downstream fall in pressure.
When breathing spontaneously, inspiratory flow occurs by creating a small negative pressure in the alveoli (~ 2-3 cm H2O below atmospheric).
This is brought about by contraction of the diaphragm and external intercostals.
Question: What generates the positive pressure in the alveoli for expiration?
Answer: The elastic recoil of the lungs and chest wall, utilizing some of the energy used during inspiration.
