Axons branch as they enter a muscle, and control the activity of a variable number of muscle fibres. The motor neurone and the muscle fibres it controls is termed the motor unit (Fig 1).
The size of motor units vary according to the degree of muscle control required.
Muscles designed for fine, delicate movements have smaller units. The extrinsic muscles of the eye are an example of this, where as few as 6-10 muscle fibres are supplied by a single motor neurone (Fig 2).
When fine control of a movement is not required, motor units are large. For example, in the gastrocnemius muscle of the calf a motor unit may contain up to 2000 muscle fibres (Fig 3).
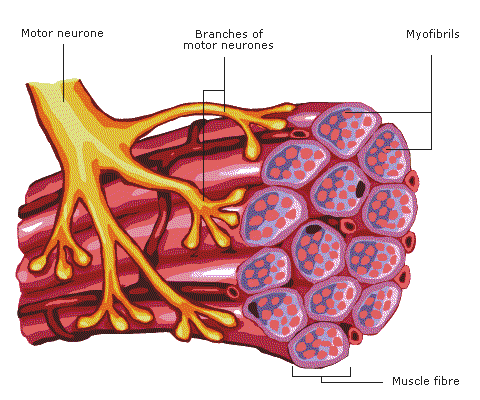
Fig 1 The motor unit
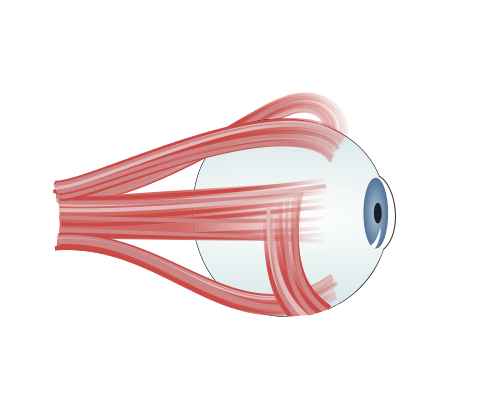
Fig 2 Extrinsic muscles of the eye
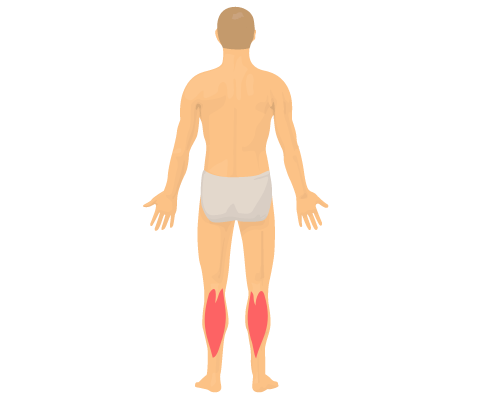
Fig 3 Gastrocnemius muscles