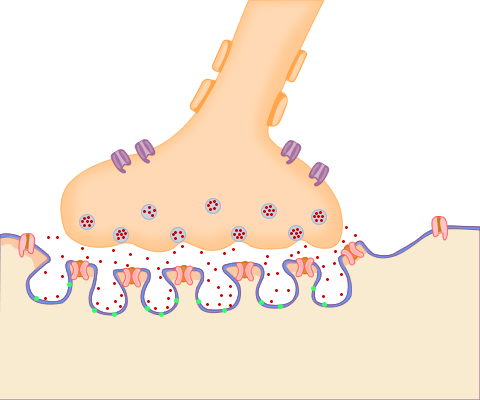
The motor neurone loses its myelin sheath as it approaches the muscle. It makes contact with the muscle at the motor end plate (Fig 1).
Synaptic vesicles are found within this terminus, concentrated near active zones. They contain the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh). Each vesicle contains about 10 000 molecules of ACh. As the nerve terminal is depolarised with the incoming action potential, voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open, which trigger release of ACh from the vesicles.
ACh molecules pass across the synaptic cleft to combine with receptors in the post-synaptic membrane. These are concentrated in crests which overlap the presynaptic active zones.
In the post-synaptic area are junctional folds which contain high concentrations of the enzyme acetylcholinesterase. Acetylcholinesterase is responsible for the breakdown of ACh.