The Acetylcholine Cycle
The synthesis of ACh involves the reaction of choline with acetyl co-enzyme A. Much of the choline used in this process is recycled but it can also be synthesized de novo in the neurone. This reaction is catalysed by the enzyme choline acetyltransferase (Fig 1).
Once ACh has combined with the receptor site, it must be rapidly removed from the synapse for repolarisation to occur. It is therefore catalyzed by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase to produce choline and acetate.
As previously mentioned, the choline is then recycled back into the terminal to produce new molecules of ACh.
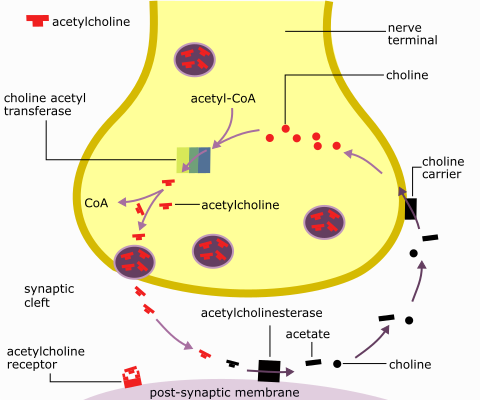
Fig 1 The acetylcholine cycle