Overview
The autonomic nervous system (ANS) consists of afferent and efferent pathways in the central and peripheral nervous systems (Fig 1).
The sensory afferents transmit sensory information from visceral structures, and chemical and mechanical data from chemoreceptors and pressure receptors.
The efferent part of the ANS is concerned with the control of cardiac muscle, smooth muscle and glands.
The central components of the ANS are in the midbrain and the medulla, and include the limbic system (emotion), the hypothalamus, and parts of the brainstem and spinal cord.
There are two main divisions, which are often antagonistic:
- The sympathetic nervous system (SNS)
- The parasympathetic nervous system (PNS)
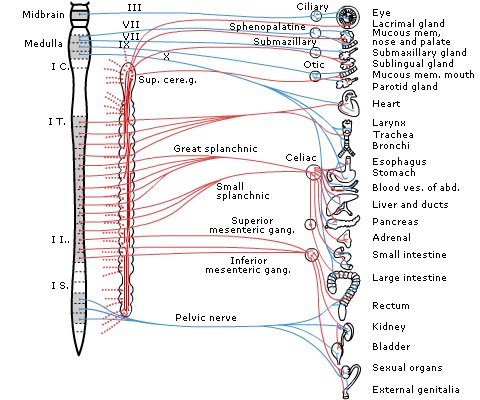
Fig 1 The efferent pathways of the autonomic nervous system