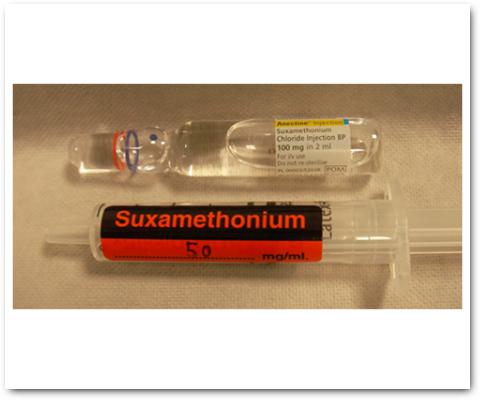
Control of Airway
The take-off phase of anaesthesia, using an IV agent, produces rapid induction of anaesthesia to a level deep enough for the anaesthetist to control the airway, and then a volatile agent is introduced to maintain anaesthesia.
Figs 1 to 4 illustrate airway maintenance steps and considerations:
- Using chin tilt and/or jaw lift (Fig 1)
- Using a guedal airway (Fig 2)
- Inserting a laryngeal mask (Fig 3)
- Use of muscle relaxants to intubate the trachea (Fig 4)
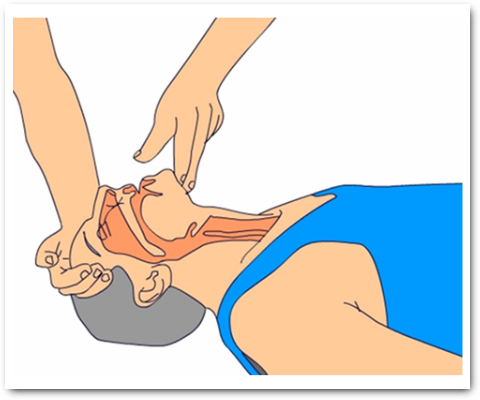
The take-off phase of anaesthesia, using an IV agent, produces rapid induction of anaesthesia to a level deep enough for the anaesthetist to control the airway, and then a volatile agent is introduced to maintain anaesthesia.
Figs 1 to 4 illustrate airway maintenance steps and considerations:
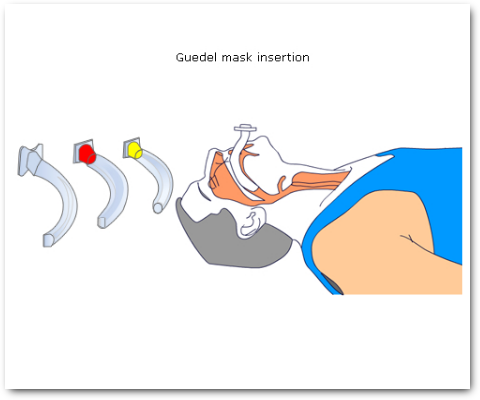
The take-off phase of anaesthesia, using an IV agent, produces rapid induction of anaesthesia to a level deep enough for the anaesthetist to control the airway, and then a volatile agent is introduced to maintain anaesthesia.
Figs 1 to 4 illustrate airway maintenance steps and considerations:
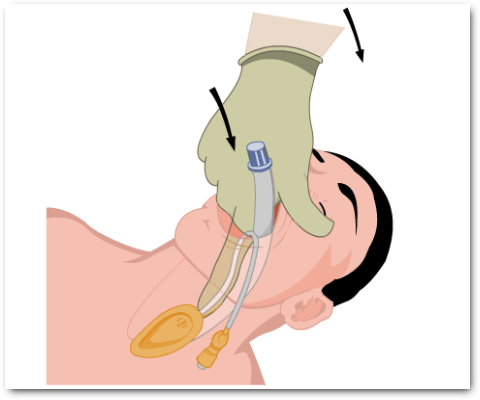
The take-off phase of anaesthesia, using an IV agent, produces rapid induction of anaesthesia to a level deep enough for the anaesthetist to control the airway, and then a volatile agent is introduced to maintain anaesthesia.
Figs 1 to 4 illustrate airway maintenance steps and considerations: