Questions and Answers
Question: What chemical class does propofol belong to and what physicochemical properties does it have?
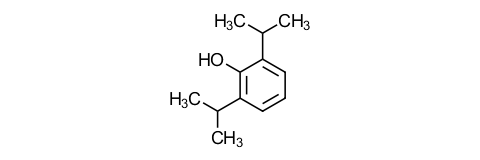
Question: What chemical class does propofol belong to and what physicochemical properties does it have?
Answer: It is a phenol derivative and extremely lipid-soluble, more so than thiopental. It has a pKa of 11, so exists almost entirely in the unionized, i.e. more lipid-soluble, form. About 98% is bound to plasma proteins.
Question: What is the dose of propofol for induction of anaesthesia?

Question: What chemical class does propofol belong to and what physicochemical properties does it have?
Answer: It is a phenol derivative and extremely lipid-soluble, more so than thiopental. It has a pKa of 11, so exists almost entirely in the unionized, i.e. more lipid-soluble, form. About 98% is bound to plasma proteins.
Question: What is the dose of propofol for induction of anaesthesia?
Answer: 1-2.5 mg/kg.
Question: What is in the ampoule of propofol?

Question: What chemical class does propofol belong to and what physicochemical properties does it have?
Answer: It is a phenol derivative and extremely lipid-soluble, more so than thiopental. It has a pKa of 11, so exists almost entirely in the unionized, i.e. more lipid-soluble, form. About 98% is bound to plasma proteins.
Question: What is the dose of propofol for induction of anaesthesia?
Answer: 1-2.5 mg/kg.
Question: What is in the ampoule of propofol?
Answer: A lipid emulsion of propofol together with an emulsifying agent, i.e. egg phosphatide, and glycerol. The emulsion contains 1% propofol, i.e. 10 mg/ml.
