Questions and Answers
Question: What chemical class does thiopental belong to and what physicochemical properties does it have?
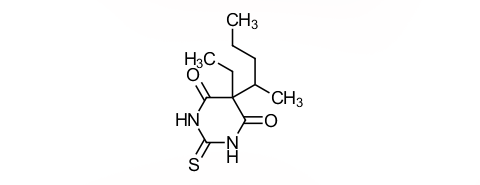
Question: What chemical class does thiopental belong to and what physicochemical properties does it have?
Answer: It is a thiobarbiturate, highly lipid-soluble and a weak acid with a pKa of 7.6. Approximately 60% of free thiopental is in the unionized form, which is more lipid-soluble. About 75-80% is bound to plasma proteins.
Question: What is the dose of thiopental for induction of anaesthesia?

Question: What chemical class does thiopental belong to and what physicochemical properties does it have?
Answer: It is a thiobarbiturate, highly lipid-soluble and a weak acid with a pKa of 7.6. Approximately 60% of free thiopental is in the unionized form, which is more lipid-soluble. About 75-80% is bound to plasma proteins.
Question: What is the dose of thiopental for induction of anaesthesia?
Answer: 3-7 mg/kg.
Question: What is in the vial of thiopental?

Question: What chemical class does thiopental belong to and what physicochemical properties does it have?
Answer: It is a thiobarbiturate, highly lipid-soluble and a weak acid with a pKa of 7.6. Approximately 60% of free thiopental is in the unionized form, which is more lipid-soluble. About 75-80% is bound to plasma proteins.
Question: What is the dose of thiopental for induction of anaesthesia?
Answer: 3-7 mg/kg.
Question: What is in the vial of thiopental?
Answer: The vial contains 500 mg of the thiopental sodium salt, together with sodium carbonate and is stored under nitrogen. When mixed with 20 ml of sterile water it forms a 2.5% solution (25 mg/ml) at pH 10.5. This high pH is required to stop the insoluble acid from precipitating out of solution.
