Animation/Interaction loading...
Coronary Steal
Fig 1 shows the coronary arteries.
A stenosed coronary artery receives a smaller proportion of coronary flow than a normal vessel. Distal to the stenosis there will be compensatory vasodilatation to maximize flow to myocardial tissue.
Isoflurane causes vasodilatation of normal coronary arteries. The animation in Fig 2 shows how blood may be diverted away from the stenotic vessel by vasodilatation of normal vessels. As a result, cardiac muscle supplied by the stenosed coronary vessel may become ischaemic.
In practice, as long as the coronary perfusion pressure is maintained, coronary steal does not seem to be a factor in perioperative myocardial ischaemia.
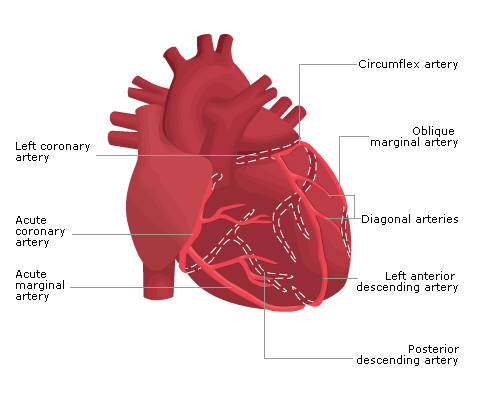
Fig 1 Coronary arteries of the heart
Fig 2 Diversion of blood away from the stenotic vessel