pKa and pH
The unionized form of the local anaesthetic must cross the axonal lipid membrane to reach the inside. Once inside, it is the ionized form of the drug that is effective in blocking the channel. The more unionized, the more rapid the passage across the membrane and the faster the onset of block (Fig 1).
Question: What determines the proportion of any drug in the ionized form compared with the unionized form?
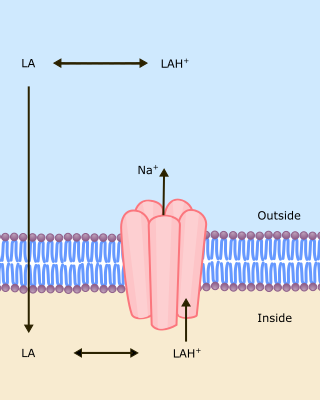
The unionized form of the local anaesthetic must cross the axonal lipid membrane to reach the inside. Once inside, it is the ionized form of the drug that is effective in blocking the channel. The more unionized, the more rapid the passage across the membrane and the faster the onset of block (Fig 1).
Question: What determines the proportion of any drug in the ionized form compared with the unionized form?
Answer: There are three factors:
- Whether the drug is a weak acid or a weak base
- The pKa of the drug, i.e. the pH at which the ionized and unionized forms are present in equal amounts
- The pH of the environment
Local anaesthetics are weak bases; weak bases are ionized below their pKa. Both lidocaine and bupivacaine have a pKa above plasma pH. At pH 7.4 both these drugs are mainly ionized, but for lidocaine approximately 25% is unionized, whereas for bupivacaine just 15% is unionized.
Question: Does this fit with the relative speed of onset of block for the two agents?

The unionized form of the local anaesthetic must cross the axonal lipid membrane to reach the inside. Once inside, it is the ionized form of the drug that is effective in blocking the channel. The more unionized, the more rapid the passage across the membrane and the faster the onset of block (Fig 1).
Question: What determines the proportion of any drug in the ionized form compared with the unionized form?
Answer: There are three factors:
- Whether the drug is a weak acid or a weak base
- The pKa of the drug, i.e. the pH at which the ionized and unionized forms are present in equal amounts
- The pH of the environment
Local anaesthetics are weak bases; weak bases are ionized below their pKa. Both lidocaine and bupivacaine have a pKa above plasma pH. At pH 7.4 both these drugs are mainly ionized, but for lidocaine approximately 25% is unionized, whereas for bupivacaine just 15% is unionized.
Question: Does this fit with the relative speed of onset of block for the two agents?
Answer: Yes. Lidocaine has a faster onset of block than bupivacaine.
